Can Good Sleep Change Your Life? The True Power of Sleep

Sleep is not a luxury—it is a biological necessity. Good sleep plays a vital role in physical health, mental clarity, emotional balance, and overall well-being. It is not just a state of rest, but an active and highly organized process in which the body and brain repair, recharge, and reset themselves.
What Is Sleep?
1. Biological Perspective
Sleep is a natural biological state in which:
-
Conscious awareness of the outside world decreases
-
Heart rate, breathing rate, and blood pressure slow down
-
The body rests, but the brain remains active
During deep sleep, the brain performs crucial tasks such as:
-
Repairing cells
-
Clearing toxins
-
Processing information through slow brain waves (delta waves)
2. Scientific Perspective
Sleep is regulated by two major systems:
Circadian Rhythm
-
Our internal 24-hour body clock
-
Controlled by light and darkness
-
Regulates the release of melatonin (the sleep hormone)
-
Signals when to sleep and wake up
Homeostatic Sleep Drive
-
Builds up the longer we stay awake
-
Caused by accumulation of adenosine
-
The longer you are awake, the stronger the urge to sleep
What Is the Real Purpose of Sleep?
1. Body Repair
-
Repairs damaged tissues and cells
-
Builds muscles and bones
-
Strengthens the immune system
-
Releases growth hormone during deep sleep
2. Brain Detox & Mental Cleansing
-
Activates the glymphatic system, which removes toxic waste from the brain
-
Helps you wake up refreshed, calm, and focused
3. Memory Consolidation
-
Organizes and stores memories
-
Enhances learning, concentration, and decision-making
Why Is Sleep Called the Cornerstone of Health?
Just as a building cannot stand without a strong foundation, health cannot exist without good sleep.
Sleep as the Master Switch
-
During deep sleep, growth hormone repairs tissues
-
Lack of repair leads to chronic pain, fatigue, and weakness
Hormonal Balance
-
Poor sleep increases ghrelin (hunger hormone)
-
Reduces leptin (satiety hormone)
-
Leads to weight gain and gut issues
-
Increases cortisol, raising the risk of stress, anxiety, and diabetes
Cognitive Health
-
Poor sleep leads to accumulation of toxic proteins like beta-amyloid
-
Increases risk of memory loss and neurodegenerative diseases
Immune Protection
-
Sleep boosts cytokine production, which fights infections
-
Chronic sleep deprivation weakens immunity
Sleep is like a charging station—no supplement or superfood can replace it.
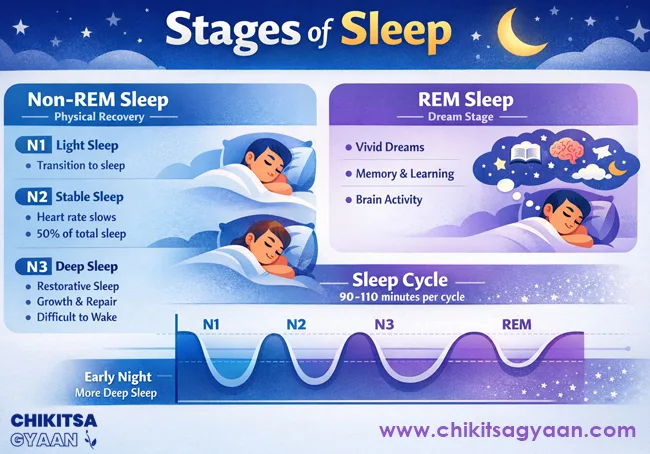
Stages of Sleep
There are two major stages of sleep:
1. Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) Sleep
Focused on physical recovery and energy conservation.
N1
-
Transition from wakefulness to sleep
-
Light sleep; lasts a few minutes
N2
-
Light but stable sleep
-
Heart rate slows, body temperature drops
-
Accounts for about 50% of total sleep
N3 (Deep Sleep)
-
Most restorative stage
-
Growth hormone release
-
Immune strengthening
-
Glymphatic system activation
-
Very difficult to wake up
2. Rapid Eye Movement (REM) Sleep
-
Dream stage
-
Brain activity resembles wakefulness
-
Emotional processing and learning occur
-
Essential for memory and mental health
Sleep Cycle
-
One cycle lasts 90–110 minutes
-
A full night includes 4–6 cycles
-
Early night: more deep sleep (N3)
-
Late night: longer REM phases
How to Improve Sleep Quality
1. Maintain Consistent Sleep Timing
-
Sleep and wake at the same time daily
-
Get sunlight exposure after waking
2. Reduce Screen Exposure
-
Avoid screens at least 1 hour before bed
-
Blue light suppresses melatonin
-
Keep the bedroom dark
3. Avoid Stimulants
-
No caffeine 6–8 hours before sleep
-
Avoid alcohol at night
-
Eat light meals; avoid oily/spicy food before bedtime
4. Create Pre-Sleep Rituals
-
Warm bath
-
Reading
-
Calm music
-
Yoga poses: Viparita Karani, Balasana, Shavasana
5. Optimize Your Sleep Environment
-
Clean, cool, quiet room
-
Indoor plants
-
Use the bed only for sleep
6. Stay Active During the Day
-
Physical activity improves sleep quality
7. Calm the Mind
-
Meditation, deep breathing, gratitude practices
Factors That Disrupt Sleep
-
Stress, anxiety, depression
-
Chronic illness
-
Smoking, alcohol, excess caffeine
-
Irregular sleep timings
-
Noise, bright light, high temperature
-
Poor food habits
Sleep Pathology: Sleep Disorders
1. Dyssomnia
Disorders affecting sleep quantity and quality:
-
Insomnia
-
Sleep Apnea
-
Narcolepsy
-
Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS)
2. Parasomnia
Abnormal behaviors during sleep:
-
Sleepwalking
-
Night Terrors
-
REM Sleep Behavior Disorder
What Is Polysomnography (PSG)?
Also known as a sleep study, PSG is an overnight diagnostic test that records:
-
Brain waves (EEG)
-
Eye movements (EOG)
-
Muscle activity (EMG)
-
Heart rhythm (ECG)
-
Breathing patterns
-
Oxygen levels
-
Snoring and body position
It helps diagnose sleep disorders accurately and guides treatment.
Final Thought
You can buy a bed, but you cannot buy sleep.
In today’s fast-paced, technology-driven life, prioritizing sleep is the real secret to long-term health.
Your health is your real wealth—and good sleep is its foundation.

